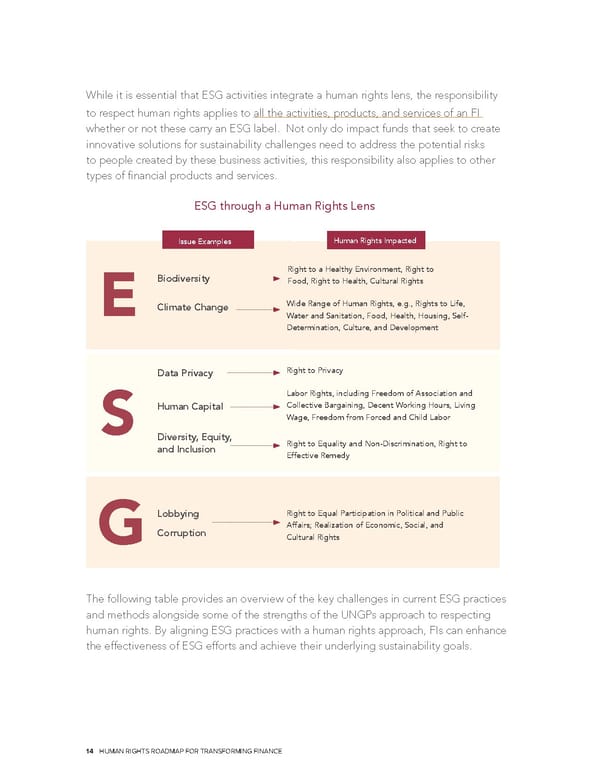
While it is essential that ESG activities integrate a human rights lens, the responsibility to respect human rights applies to all the activities, products, and services of an FI whether or not these carry an ESG label. Not only do impact funds that seek to create innovative solutions for sustainability challenges need to address the potential risks to people created by these business activities, this responsibility also applies to other types of financial products and services. ESG through a Human Rights Lens Issue Examples Human Rights Impacted Biodiversity Right to a Healthy Environment, Right to Food, Right to Health, Cultural Rights EClimate Change Wide Range of Human Rights, e.g., Rights to Life, Water and Sanitation, Food, Health, Housing, Self- Determination, Culture, and Development Data Privacy Right to Privacy Labor Rights, including Freedom of Association and Human Capital Collective Bargaining, Decent Working Hours, Living S Wage, Freedom from Forced and Child Labor Diversity, Equity, Right to Equality and Non-Discrimination, Right to and Inclusion Effective Remedy Lobbying Right to Equal Participation in Political and Public Corruption Affairs; Realization of Economic, Social, and G Cultural Rights The following table provides an overview of the key challenges in current ESG practices and methods alongside some of the strengths of the UNGPs approach to respecting human rights. By aligning ESG practices with a human rights approach, FIs can enhance the effectiveness of ESG efforts and achieve their underlying sustainability goals. 14 HUMAN RIGHTS ROADMAP FOR TRANSFORMING FINANCE
 Human Rights Roadmap for Transforming Finance Page 13 Page 15
Human Rights Roadmap for Transforming Finance Page 13 Page 15